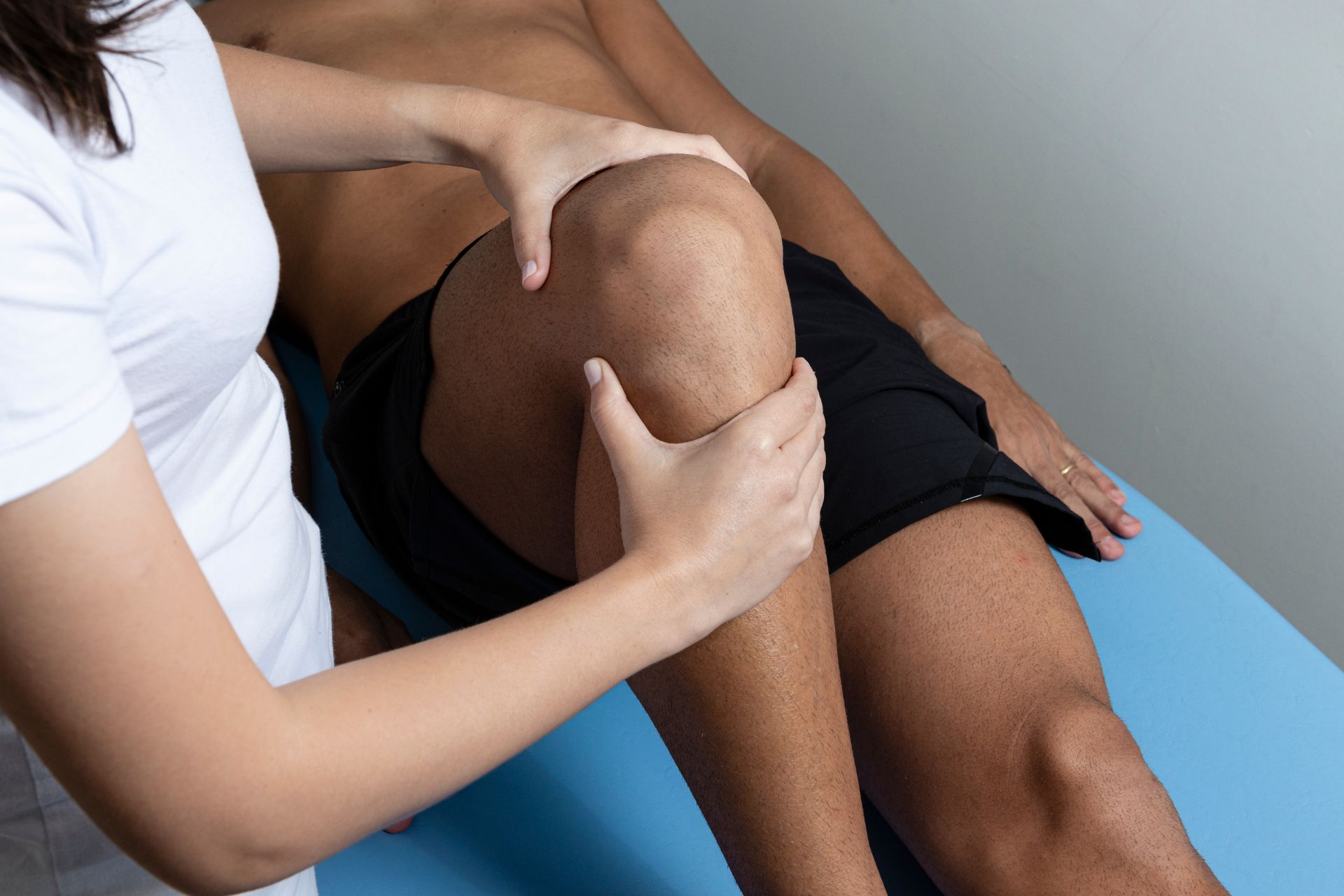
Range of Motion Testing
How is range of motion testing used in physical therapy for patients recovering from joint injuries?
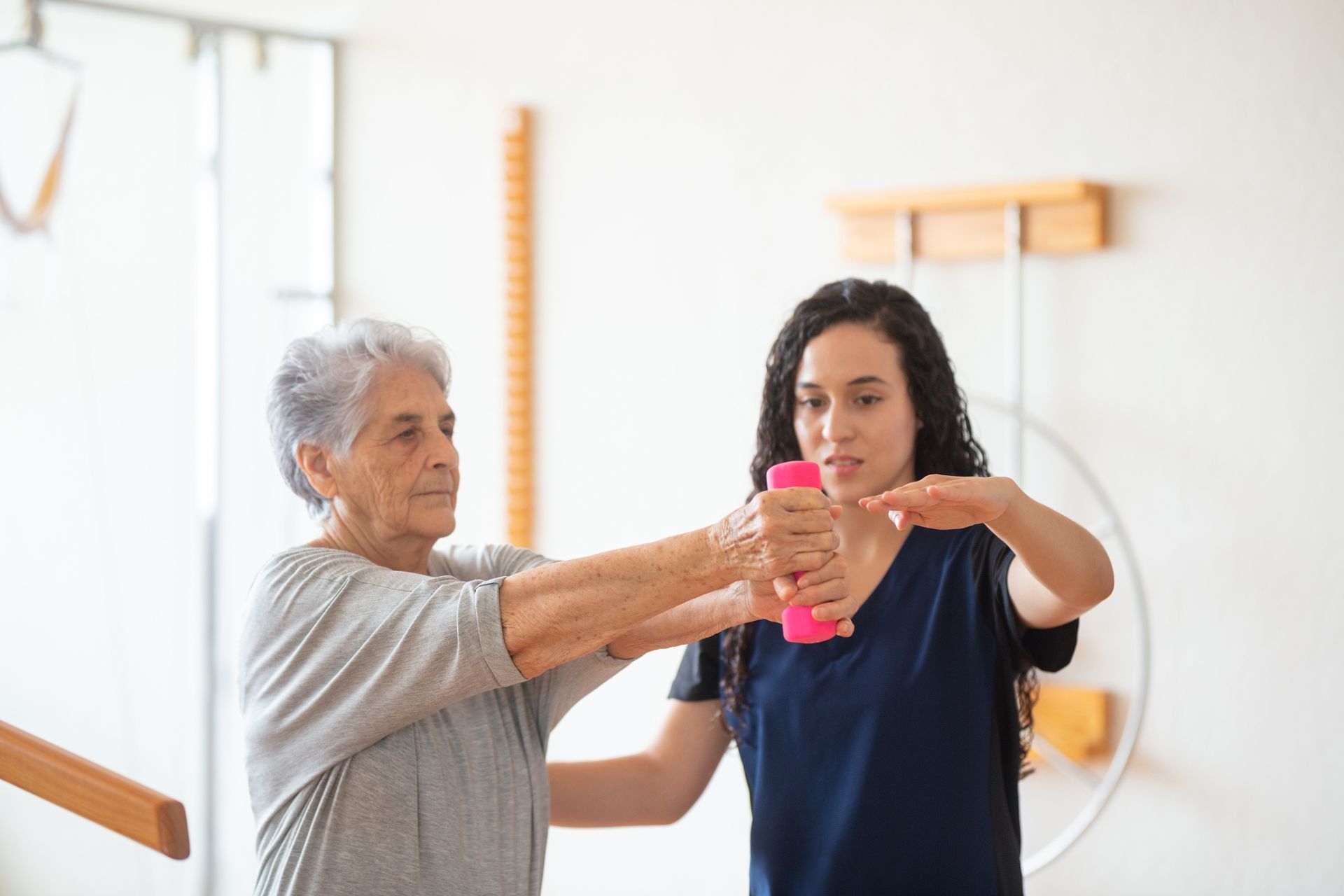
Range of motion testing is a crucial component of physical therapy for patients recovering from joint injuries as it helps therapists assess the extent of movement in the affected joint. By measuring the range of motion, therapists can track progress, identify limitations, and tailor treatment plans to improve flexibility, strength, and function in the injured joint. This testing allows therapists to monitor improvements over time and adjust therapy techniques accordingly to optimize the patient's recovery process.
Musculoskeletal Assessment and Physical Therapy